What Is Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the biological process through which green plants, algae and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy. This is a fundamental concept in both KS3 and GCSE science, as it forms the basis of most life on Earth.
The word photosynthesis comes from the Greek:
- Photo = light
- Synthesis = putting together
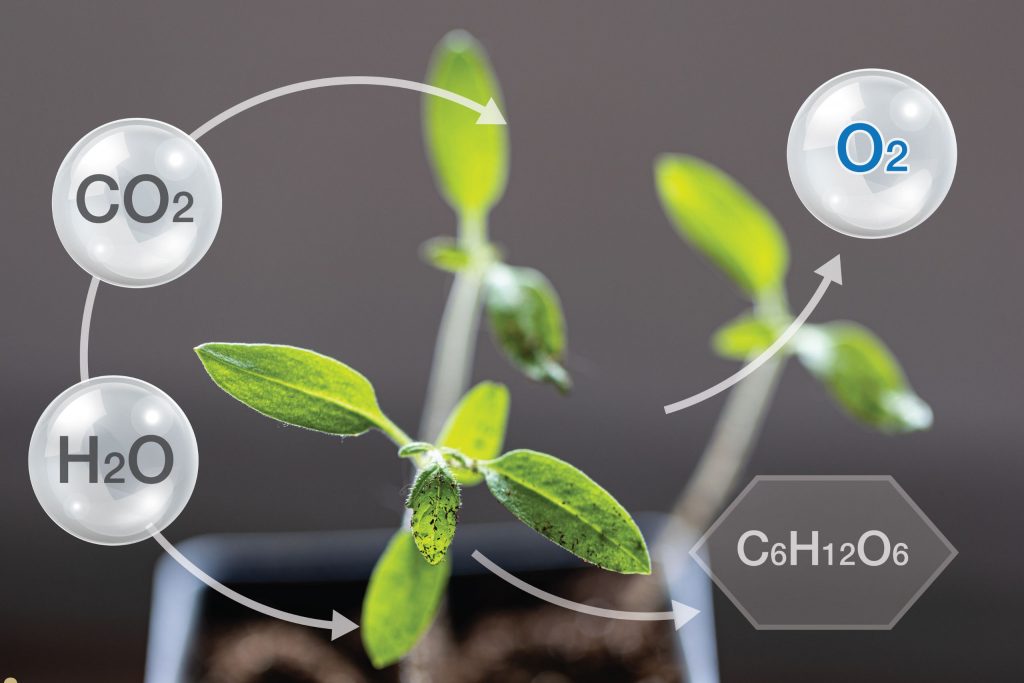
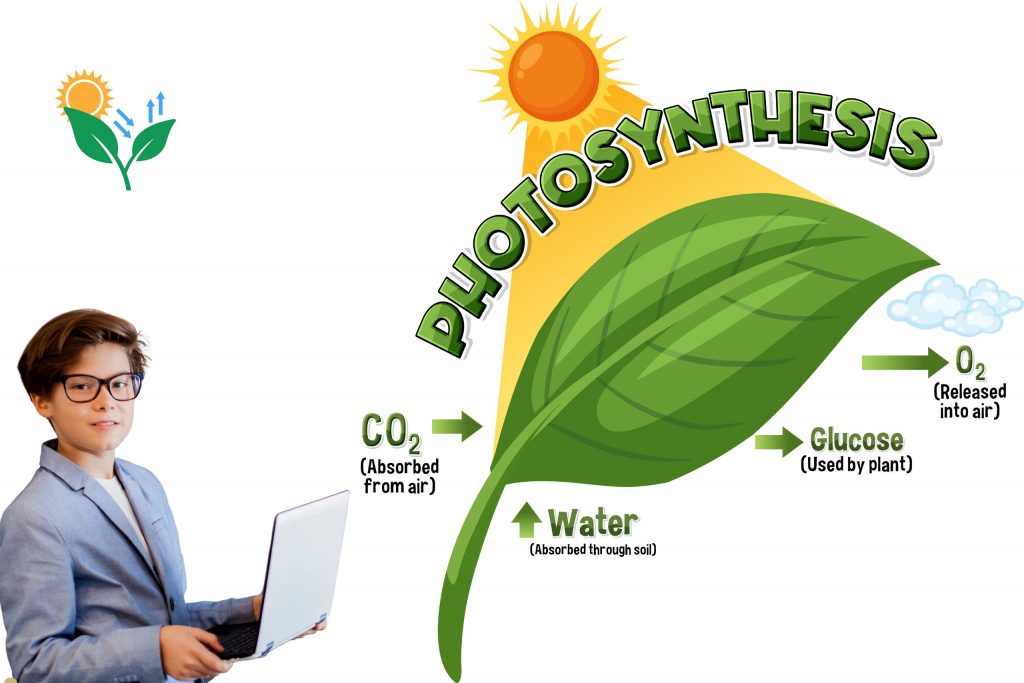
This process takes place mainly in the leaves of plants, where chloroplasts absorb sunlight using a green pigment called chlorophyll. This light energy is then used to convert carbon dioxide from the air and water from the soil into glucose and oxygen.
The Word Equation for Photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen
(in the presence of light and chlorophyll)
The Balanced Chemical Equation
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
This equation shows that six molecules of carbon dioxide and six molecules of water produce one molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen.
Where Does Photosynthesis Happen?
Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts, which are mainly found in the palisade mesophyll cells of a plant’s leaves. These organelles contain chlorophyll, the green pigment that captures sunlight. Writing Tips for GCSE English
Key Structures Involved:
- The leaf is the main site of photosynthesis.
- Stomata are pores on the underside of leaves that allow gas exchange.
- Xylem and Phloem vessels that transport water and food through the plant.
Importance of Photosynthesis in Nature
Photosynthesis is vital for life because:
- It produces oxygen, which animals (including humans) need for respiration.
- It removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping regulate the climate.
- It forms the base of most food chains – plants are known as producers.
What Do Plants Do With the Glucose Produced?
Glucose serves multiple purposes for the plant:
- Respiration is used to release energy for growth and repair.
- Storage as starch in roots, stems or leaves.
- Making cellulose to build strong cell walls.
- Producing fats and oils stored in seeds.
- Synthesis of amino acids combining glucose with nitrates from the soil.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis does not happen at a constant rate. It is influenced by several limiting factors:
1. Light Intensity
More light means more energy, leading to a higher rate of photosynthesis, up to a certain point. English Grammar Guide for KS1 & KS2
2. Carbon Dioxide Concentration
A higher level of carbon dioxide increases the rate of photosynthesis, again up to a limit.
3. Temperature
Photosynthesis is controlled by enzymes. If it’s too cold, enzymes work slowly. Too hot, and they become denatured.
4. Water Availability
Although often overlooked, water is a raw material for photosynthesis. A shortage reduces the rate dramatically.
Experiments to Investigate Photosynthesis
1. The Pondweed (Elodea) Experiment
This practical investigates how light intensity affects the rate of photosynthesis. Bubbles of oxygen are counted as the plant photosynthesises under varying light distances.
2. The Starch Test
Leaves are tested for the presence of starch (evidence of photosynthesis) using iodine. A leaf is boiled, decolourised with ethanol, and then tested. If it turns blue-black, starch is present. What is the Water Cycle?
Leaf Adaptations for Photosynthesis
Plants have evolved special features to maximise their ability to photosynthesise:
- Broad leaves provide a large surface area.
- Thin structure reduces diffusion distance for gases.
- Chloroplast-rich palisade layer absorbs the maximum amount of light.
- Veins transport water and sugars.
- Stomata regulate gas exchange.
Photosynthesis and the Carbon Cycle
Photosynthesis plays a key role in the carbon cycle. It removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and fixes it into organic molecules. When plants and animals die, decomposition returns carbon to the soil and air, maintaining the balance.
How Humans Depend on Photosynthesis
Every breath we take is thanks to photosynthesis. It supplies oxygen and is also responsible for nearly all of the food we consume, either directly from plants or indirectly through animals. Additionally, fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas were formed from ancient plant matter – all products of photosynthesis.
How Technology Enhances Photosynthesis Research
Modern technology, like infrared gas analysers, chlorophyll meters, and controlled environment chambers, helps scientists study photosynthesis in-depth. These tools are used in agriculture, climate science, and bioengineering to improve crop yields and understand environmental impacts. Enrol now for affordable Online Tutoring UK
In summary, understanding photosynthesis is essential for mastering KS3 and GCSE Science. It’s not only a key biological process but also a crucial part of life on Earth.
Photosynthesis FAQs
Q. What is the main purpose of photosynthesis?
To convert light energy into chemical energy (glucose), which plants use for growth and energy.
Q. Why is chlorophyll important?
Chlorophyll absorbs sunlight and gives plants their green colour. It’s essential for capturing light energy.
Q. How does photosynthesis help humans?
It produces oxygen for breathing and provides the base of the food chain.
Q. Can photosynthesis happen at night?
No, light is required. However, plants still respire at night.
Q. Why do plants store glucose as starch?
Starch is insoluble and doesn’t affect the plant’s water balance, making it ideal for storage.
Q. How does temperature affect photosynthesis?
Too low and the enzymes slow down. Too high and enzymes denature, halting the process.
